What is D2C and Why Should eCommerce Sellers Care?

Over the last couple of years, the consumers have come to fully control their buying journey. Consumers demand personalization and trust brands more when they can directly interact with them. Many traditional brands have started wondering what is D2C , how they can leverage this model over and above their traditional supply chain.
The major reasons for this paradigm shift in the business are:
- Digital adoption by brands and consumers.
- Increased internet penetration and accessibility.
- COVID 19 and lockdown of physical stores
- Boom in e-commerce platforms with improved logistics operations.
- Improved IT infrastructure at point of sale, payments, and logistics tracking.
- Rising disposable household income of Indian consumers.
Interestingly enough, the search trend for the phrase ‘what is D2C’ has been on the rise. Not just sellers but also buyers are trying to understand it. Thanks to shows like Shark Tank, D2C has become a household name.
What is D2C?
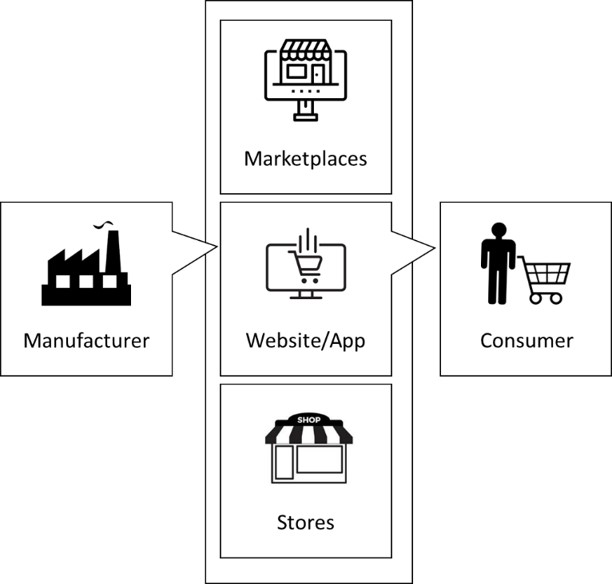
Direct to consumers (D2C) is a business model where companies reach out to consumers with no intermediaries involved. D2C brands sell products via e-commerce websites, mobile applications, retail stores, and factory outlets. By eliminating distributers and wholesalers, companies need to set up a resilient overall supply chain.
Let’s review some top D2C brands to understand what is D2C and different distribution strategies adopted by them:
- Physical stores: There are many different formats of retail stores making it tricky to classify what is D2C store. D2C brands, such as LensKart, uses company owned company operated (COCO) or franchise owned company operated (FOCO) stores to sell their products.
- Pure-Play channels and logistics: Some D2C brands use their own channels and fleet to manage sales and distribution. For ex. Licious sells its products via its own website and mobile application. Also, it controls overall supply chain by managing 200+ SKUs across the country and large fleet of logistics.
- Marketplace only: Some small brands only sell through ecommerce marketplaces like Amazon and Flipkart. These brands rely on marketplaces for operations and deliveries.
- Hybrid Omnichannel: Most of the D2C brands such as Mama Earth and Sugar Cosmetics take the hybrid omnichannel approach by selling through own website, stores, digital channels and ecommerce marketplaces. Orders from own digital channels are delivered by brand fleet or 3PL last mile delivery providers like Delhivery.
Why D2C Companies Should Focus On Building Their Own Brand?
After understanding what is D2C, let’s explore how companies can go the D2C route. Let us also explore the pros and cons of different channels.
Ecommerce marketplaces play a great role in the D2C market. According to Forrester Research, by end of 2021, Amazon had a user base of over 100 million and Flipkart of over 350 million. Together they provide a huge customer base that sellers can tap into.
Becoming D2C by leveraging marketplaces is the easiest approach. Sellers only need to register them and update their products with details. With policies such as fulfilment by Amazon (FBA) these marketplaces take care of all the operations and deliveries.
However, Flipkart or Amazon may be an easy place to start selling, but they have their own challenges too. While a lot of new brands first choose marketplaces to reach customers, companies soon realize the importance of building their own channels and distribution capabilities.
Let’s deeper dive into why ecommerce sellers should care about selling via own channels versus marketplaces:

Autonomy Over Operations
Full Control Over Supply Chain
The answer to why and what is D2C is reaching directly to customers, which basically means full control over supply chain. Companies with their own channels don’t need to pay commissions to marketplaces for their operational support. Companies can do the deliveries with own fleet or appoint third-party logistics providers of their choice.
No Constraints of Marketplace Rules
On third-party platforms, sellers need to follow the marketplace’s rules. Many sellers face temporary or permanent ban if they break certain rules.
Amazon and Flipkart have stringent rules for returns, exchanges, and warranties. Sellers have to abide by them even if reduces their profits.
Marketplaces even have the right to change the rules or the entire site structure overnight. Thus, D2C brands that rely on the marketplace will have to work within constraints.
No Competition on Your Own Website
When people search for something, marketplaces list hundreds of products from different sellers.
But in the case of the brand’s own online store, buyers will see the items only offered by the brand. Besides, buyers can see all the various design choices and variants of each product.
Focus on Customers and Brand Building
More Access to Customer Data
If you ask a D2C-first company, what is D2C, they will describe it as a customer-centric business model. Collecting customer data is the biggest advantage of becoming a D2C brand. On marketplaces, sellers never have full ownership of customers’ data. Marketplaces do provide purchase history, transactional data, and basic customer information. Privacy rights policies have also brought about changes in rules about storing customer data.
But with their own website, brands can go beyond this data. Companies can set up analytical tools to know how people spend time on the website, track customer buying journeys, and much more.
This will help brands to provide a personalized customer experience and increase sales.
Higher Brand Resonance
Selling directly to the customers, helps companies to establish their a brand image. When customers buy from a brand’s website, they automatically connect with the brand.
Also, full access to customer journey and data provides a great opportunity for the brand to build strong relationships.
Improved Product Recommendations
Amazon and Flipkart both do an amazing job at pushing people to buy. However, they create their own versions of best-selling or similar product listings. These lists might also include competitors’ products and can actually result in losing customers. While this is part of business, it can hit small scale sellers drastically.
This won’t be an issue if D2C brands have their own digital channels. Brands can build their custom build product recommendation engines to upsell and cross-sell products to their existing customers.
Cost Reduction and Increasing Sales
No Fees and Commissions
Registering on Amazon or Flipkart is easy but operations come at a heavy fee. They charge “referral fees” for granting access to their massive audience base. Also, marketplaces keep a huge share of each sale, done using their platform.
With their own website, companies won’t need to worry about paying massive cuts off their sales. Companies can spend more on marketing and branding activities.
Personalized Campaigns for More Sales
Referrals or coupons are very effective as they help brands to reach new customers who may be hearing about them for the first time. One their own e-commerce channels, brands have the freedom to run these campaigns.
Also, by analyzing the customer journey, brands can run retargeting or incentive based campaigns to convert customers.
Conclusion
D2C segment seems to be rapidly growing, especially in India. India has become the 4th largest D2C market in the world following the US, China, and Japan. According to are by Avendus , by the end of 2021, India already was home to 600+ D2C brands. And the growth suggests that the total addressable market will be a $100 Bn opportunity by 2025.
Thus, it is a high time for companies to understand what the D2C model and take steps towards becoming a D2C brand. Also, to sustain in the fast-changing market, D2C companies need to be self-reliant and focus on building their own channels and brand.
Some of the major activities that can help D2C brands to attract customers to their own stores are:
- Providing personalized customer experiences using data.
- Building trust through reviews.
- Building a personal brand.
- Expanding distribution to different geographies.
- Building strong customer relationships.
- Promotions on social media and other digital platforms.
- Offering referrals and coupon codes that only work on brand websites or stores.
- Offering store-exclusive products.
